Text
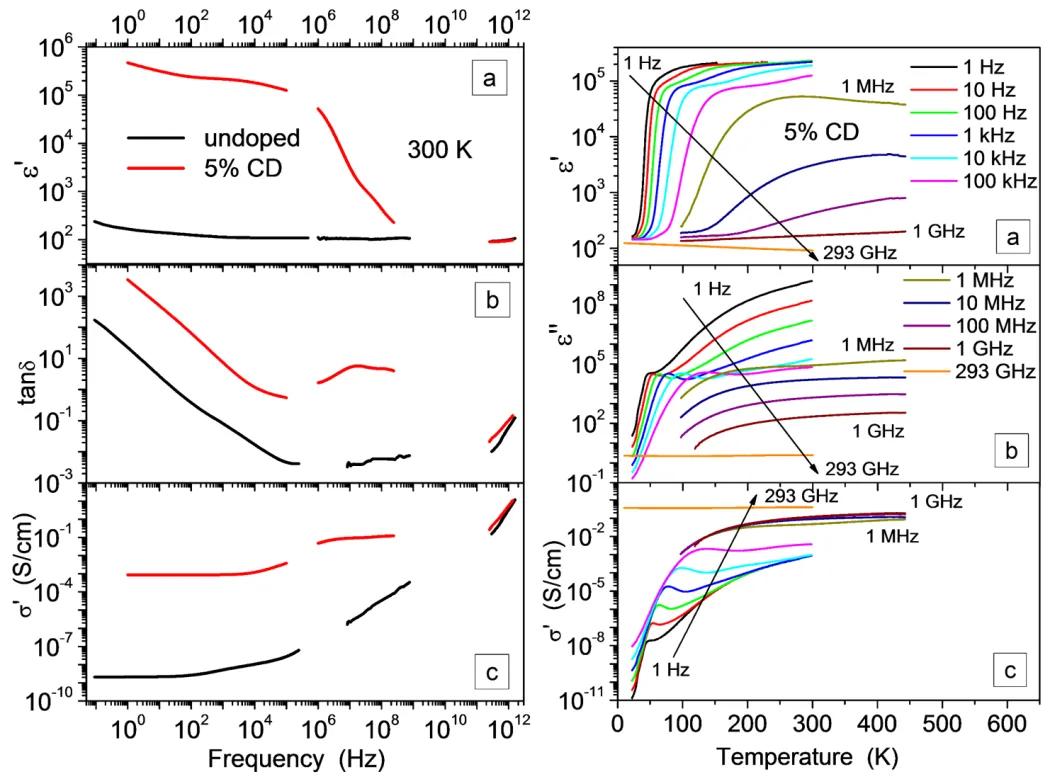
The dielectric response of ceramics of co-doped rutile Ti1-x(Nb0.5In0.5)xO2 has been measured via a combination of impedance, high-frequency coaxial, THz transmission, and IR reflectivity spectroscopies spanning 15 decades of frequency between 0.1 Hz and 240 THz. It is argued that the colossal dielectric permittivity reported by other authors can be explained by a combination of thin low-conducting grain boundaries and low-conducting depletion near-electrode layers which give rise to thermally activated dielectric relaxations in higher radiofrequency and low-frequency ranges, respectively.
Contact person: Jan Petzelt
Cooperating institution: Brock University, Ontario, Canada